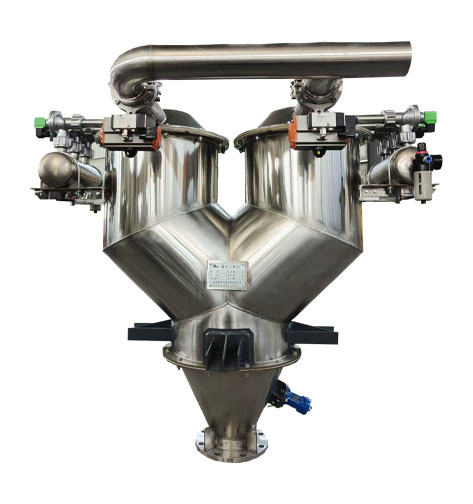
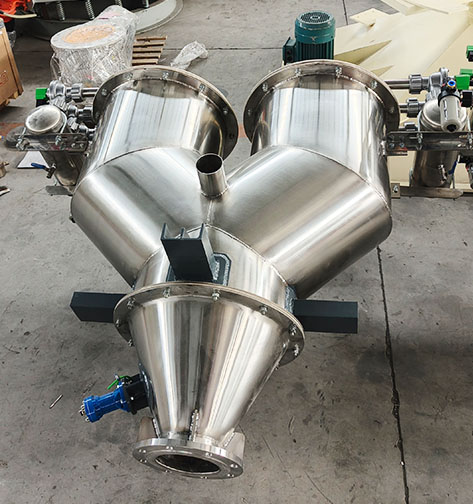
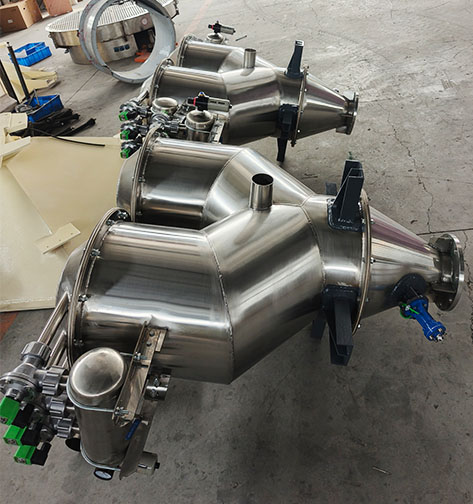



The dual-head vacuum feeder is a continuous negative pressure conveying model developed to adapt to the vacuum conveying of powder and granular materials over longer distances. The dual-hopper continuous vacuum feeder is composed of a vortex vacuum pump, two vacuum hoppers, a three-way inlet, etc.
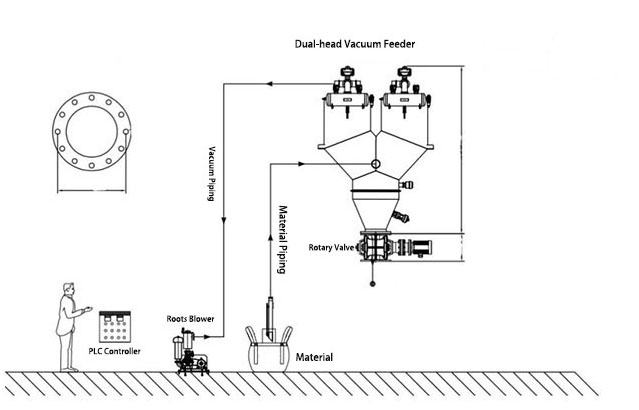
1. The dual-head design (alternating operation or collaborative operation) can simultaneously load two material bins, significantly enhancing production efficiency.
2. Pulse reverse blowing ensures no material remains in the pipes, maintaining a high level of cleanliness.
3. The entire machine is wear-resistant and corrosion-resistant, ensuring a long service life.
4. It features excellent sealing performance, effectively preventing material leakage and dust dispersion, ensuring a clean working environment.
5. Utilizing vacuum adsorption principles, it causes minimal damage to materials, making it particularly suitable for fragile and easily agglomerated materials.
6. The equipment is easy to operate, highly automated, and can precisely control material loading based on production needs, reducing manual intervention and improving the stability and reliability of production.
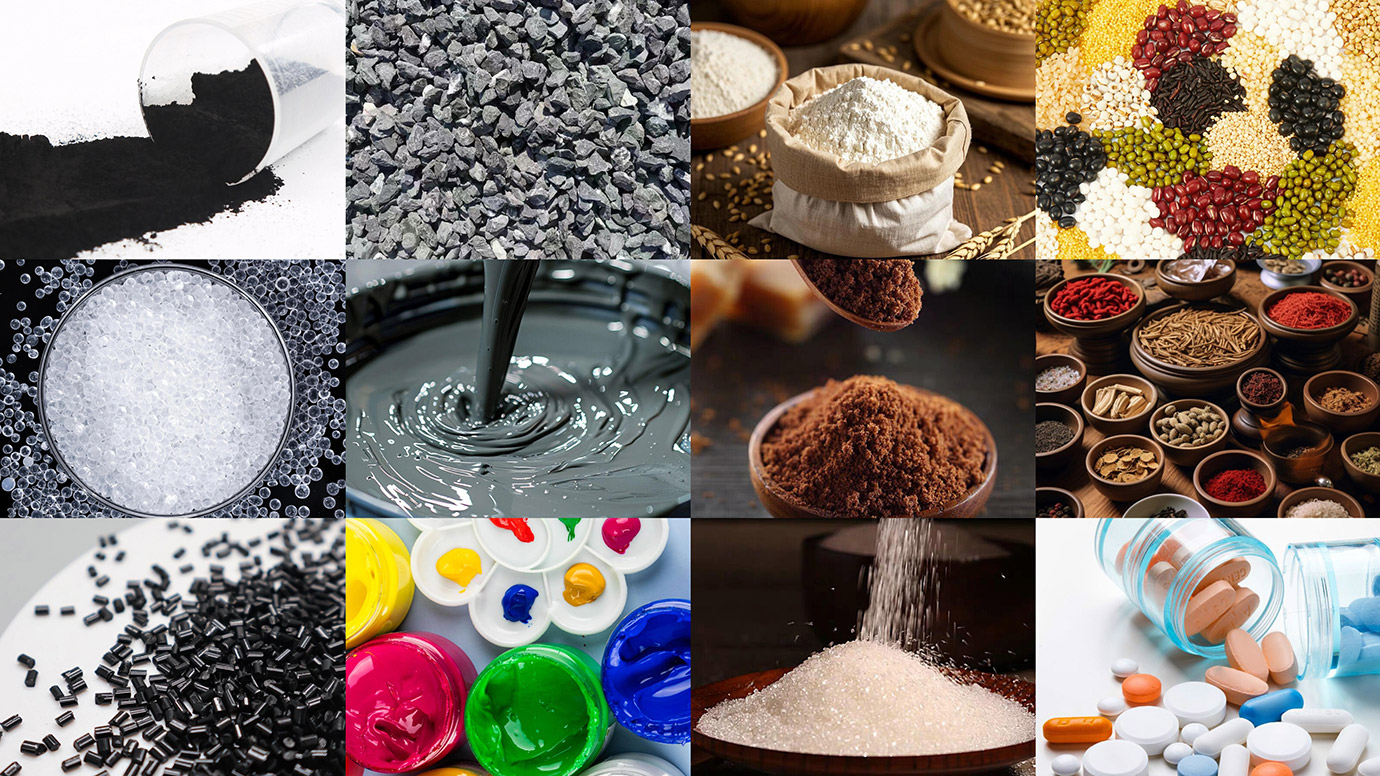
1. Pharmaceutical industry: Transfer of raw materials, intermediates, tablets, granules, capsules, and powders. Compliant with GMP standards, it prevents cross-contamination and is suitable for aseptic production environments.
2. Chemical industry: Closed transfer of materials such as resins, pigments, catalysts, plastic particles, and rubber powder. Explosion-proof design suitable for flammable, explosive, or volatile chemicals.
3. Food industry: Hygienic transfer of materials such as flour, sugar, milk powder, additives, seasonings, and grain particles. Materials comply with food-grade certifications (such as 304/316 stainless steel).
4. New energy and new materials: Dust-free transfer of fine powders such as positive and negative electrode materials for lithium batteries (such as graphite, lithium cobalt oxide), photovoltaic materials (silicon powder), and nanomaterials.
5. Other industries: Pesticides, veterinary drugs, feed, ceramic powders, building materials (such as cement additives), etc.

The RN series ultrasonic vibrating screen is a high-precision and high-stability RN ultrasonic vibrating screening...
Learn MoreThe design of the circular swing screen is a high-efficiency screening machine specially designed to meet the...
Learn MoreThe rotary vibrating screen uses weights (unbalanced weights) installed at the upper and lower ends of the vibration motor to...
Learn MoreThe dust-free feeding station solves the dust problem in the feeding station and mainly consists of...
Learn MoreThe fully enclosed dust-free ton bag feeding station has a simple structure and a high degree of automation...
Learn MoreThe open-top dust-free ton bag feeding station uses an electric hoist to lift the material bag to the feeding port...
Learn MoreThe vacuum feeding machine can automatically transport various materials to the hoppers of packaging machines...
Learn More